Research Work
-
2010.8 - Now
National Centre for Computer Animation, The Media School, Bournemouth University, UK
Research Topic: VR-based simulation system in laparoscopic rectum surgery
(Cooperated with Poole Hospital and Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch Hospitals)
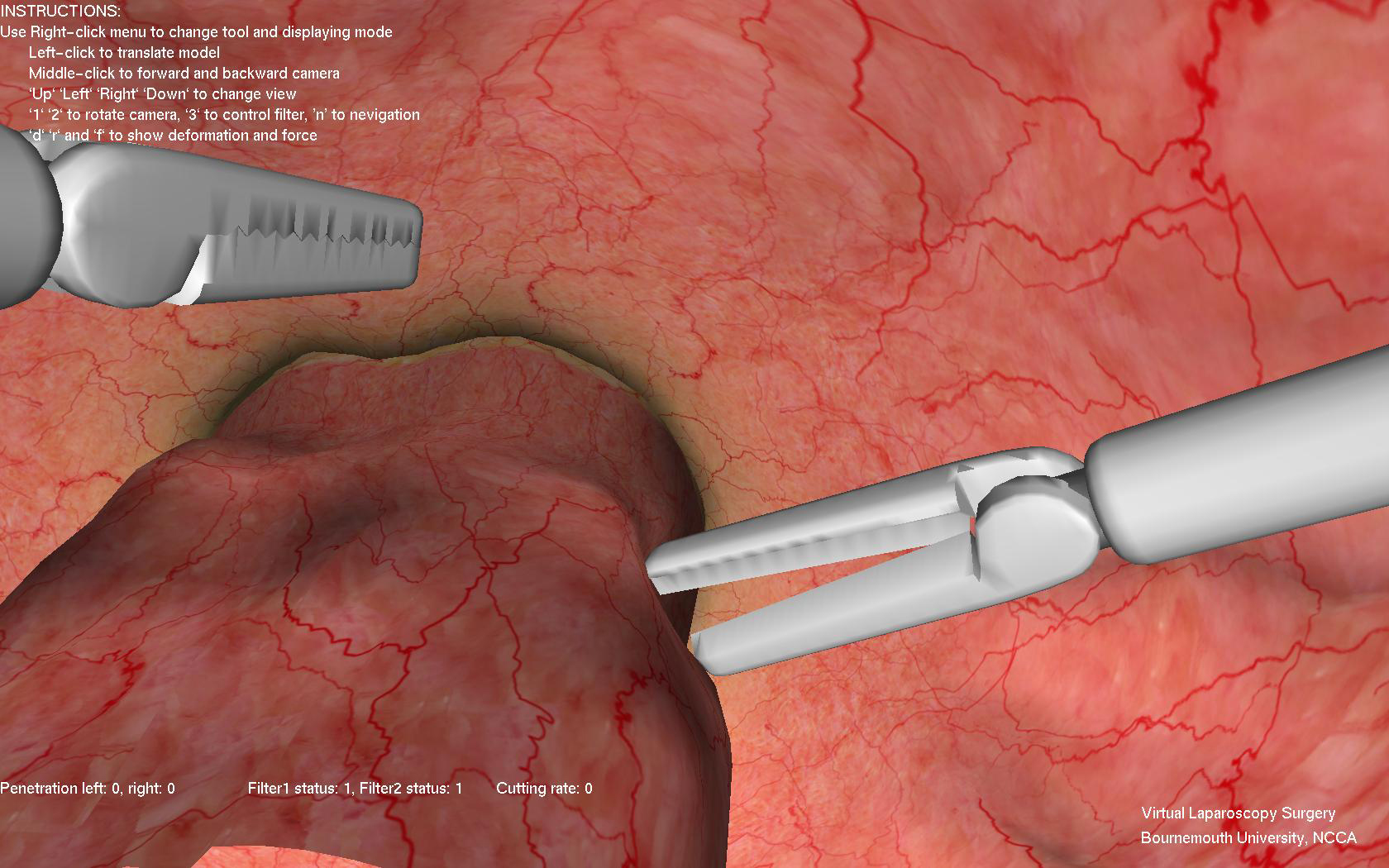
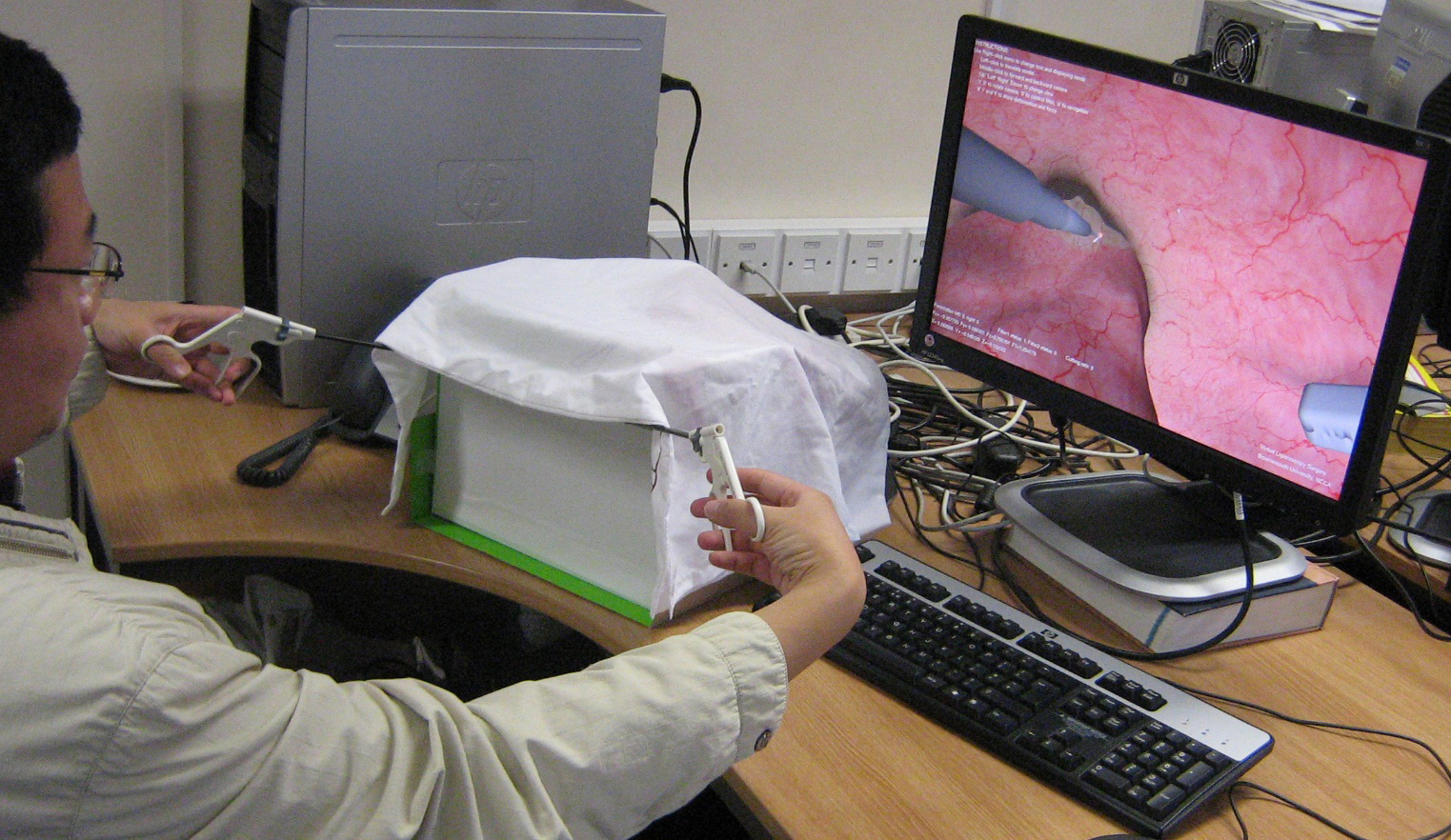
Detail: Compared with traditional open surgery, minimally invasive surgery (MIS) is less in surgical trauma, less post-operative pain and a shorter convalescence for patients. In the last ten years, in particular, laparoscopic colorectal surgery has witnessed a shift from open surgery to the laparoscopic approach. This project is developing a virtual simulation system for the rectum cancer surgery. It can be used to train the laparoscopic surgeons. The hardware of system is composed of a computer, a display screen and two haptic devices (Phantom Omni). The haptic device provides 6-DOF navigating parameters (pitch, yaw, insertion) and force feedback when there is a collision detected. Run-time operations include soft tissue deformation, collision detection, cutting, rendering and the communication with the haptic devices. Some novel techniques are applied in this system. Throughout the whole system development process, three consultant surgeons from the Bournemouth and Poole Hospitals (NHS, UK) have been closely involved. They both advise our researchers about the medical content and help evaluate the results.
Demos:
1.video (mpg)
- 2006.9 - 2010.2 National Centre for Computer Animation, The Media School, Bournemouth University, UK
1) Research Topic: Sketch-based cartoon and 2D motion capture (PhD thesis)
Detail: In current 2D animation (cartoon) production, the generation of key-frames and in-between frames are the two most important and labour intensive steps. Although some commercially available software tools, e.g. Animo and Toon Boom, have been helpful in generating in-between frames, they often lack ‘personality’. In practice, many in-betweens are still created manually. So far little exists in the market to help key-framers to produce their work more efficiently. Inspired by 3D animation techniques, we have developed a prototype system with a very simple user interface to improve the degree of automation for the production of 2D animation without sacrificing the quality. Our technique is characterized by two special features - sketch-based; and skeleton-driven. This has two parts: Part 1: cartoon sequence generation and Part 2: motion capture and reuse. We anticipate that this technique will be not only of interest to professional cartoon studios, but also to novice 2D artists for creating 2D moving graphics.
Demos:
- Video (rmvb) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m_8V9onN2HQ
- Presentation (ppt)
2) Research Topic: Automatic rigging and skinning for animated character
Detail: Animating an articulated 3D character requires the specification of its interior skeleton structure which defines how its motion deforms the skin surface. Currently this task is conducted by manual work, which normally needs special expertise for animators to finish a good result for character animation. We present an automatic rigging method making use of a new geometry entity called the 3D silhouette. By avoiding complicated computation such as voxelization and pruning, this approach is simple and efficient, much faster than existing methods. This is very useful for quick animation production, with applications including games design and prototype graphical systems.
Demos:
- Video (rmvb)
- Presentation (ppt)
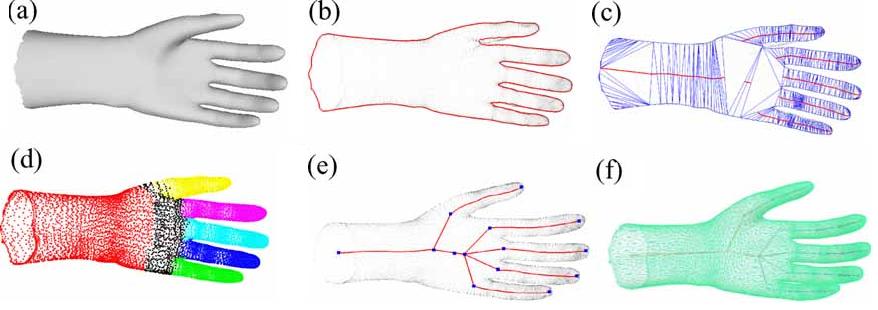
3) Research Topic: Fast character modeling with sketch-based PDE surfaces
Detail: Virtual characters are commonly used in computer games and computer animated films. Model building of virtual characters is usually a labor expensive task. How to simplify the modeling of a complex virtual character and create the model quickly is of practical significance. Current popular modeling systems are effective in creating various geometric models. However, they are not always best fitted with the practice exercised by artists. In this project, we presented a new modeling framework which divides the task into two subtasks: global modeling and local modeling. The global models are created from projected profiles by hand-drawn sketches. The local modeling uses generalized elliptic curve based surfaces and partial differential equation (PDE) surfaces to generate the detail of models. Working with two research fellows in NCCA, I was in charge of global modeling by sketch profiles in this project.
-
2003.9-2006.4 The Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Speech and Image Information Processing, School of Computer Science, Northwestern Polytechnical University, P. R. China
Research Topic: 3D visualization, measurement and simulation in craniofacial surgery (MSc thesis)
Project: Supported by the Technology Innovation Fund in Shaan xi Province, this research project is cooperated with the Stomatology Hospital of Xi an Jiaotong University. 3D measurement and visualization of the cranium is an important research area in modern orthodontics and craniofacial plastic surgery. In this project, we coped with three tasks: 3-d reconstruction of the skull by X-rays, 3-d measurement of the face by 3-d laser scanner and craniofacial surgery simulation based on finite element. Using three X-ray pictures, we reconstruct the 3D skull by correlated vision, which is a low radiation, low cost alternative to CT-based system. We also designed a supervised learning method to estimate the soft tissue stiffness parameters in surgery simulation. In the end, we completed a software tool package and published related papers in journal and international conferences.